In today’s data-driven world, businesses that harness external data gain a significant competitive edge. External data, derived from sources outside the organization, can provide insights that internal data alone cannot offer.
77% say data-driven decision-making is increasingly important for data and analytics professionals. [source]
40% of enterprises worldwide (50% in the US) say using data and intelligence strategically to create competitive differentiation is a key critical lever to running a digital business
74% of enterprises are utilizing location data to create intelligent context [source]
External data refers to information generated outside an organization’s internal systems that provides real-world context to business performance. Unlike internal data—such as sales, CRM records, or operational metrics—external data captures market forces, environmental factors, and human behavior that influence outcomes but are not directly observable from within the enterprise.
In practical terms, external data answers questions internal data cannot, such as:
- Why demand shifted in a specific region
- What external events influenced customer behavior
- When conditions are likely to change again
When integrated correctly, external data transforms analytics from descriptive reporting into forward-looking, decision-ready intelligence.
The Benefits of External Data
1. Market Insights
External data provides a broader perspective on market trends, customer behavior, and the competitive landscape. By analyzing industry reports, social media trends, and market research, businesses can identify opportunities and threats that might not be visible through internal data alone.
2. Customer Understanding
Access to external customer data, such as social media activity, purchase behavior, and demographic information, helps businesses create more accurate customer profiles. This enhances personalized marketing efforts, leading to higher customer engagement and satisfaction.
3. Improved Decision-Making
Combining internal data with external sources like economic indicators, weather patterns, and geopolitical events can improve the accuracy of predictive models. This leads to better forecasting and more informed strategic decisions.
4. Risk Management
External data can identify potential risks, such as supply chain disruptions, regulatory changes, and economic downturns. By integrating this data into risk management strategies, businesses can mitigate risks more effectively and ensure continuity.
5. Innovation and Product Development
Insights from external data sources can inspire innovation and drive product development. Understanding emerging trends, customer needs, and technological advancements allows businesses to stay ahead of the curve and deliver products that meet market demands.
Why Businesses Need a Data Strategy
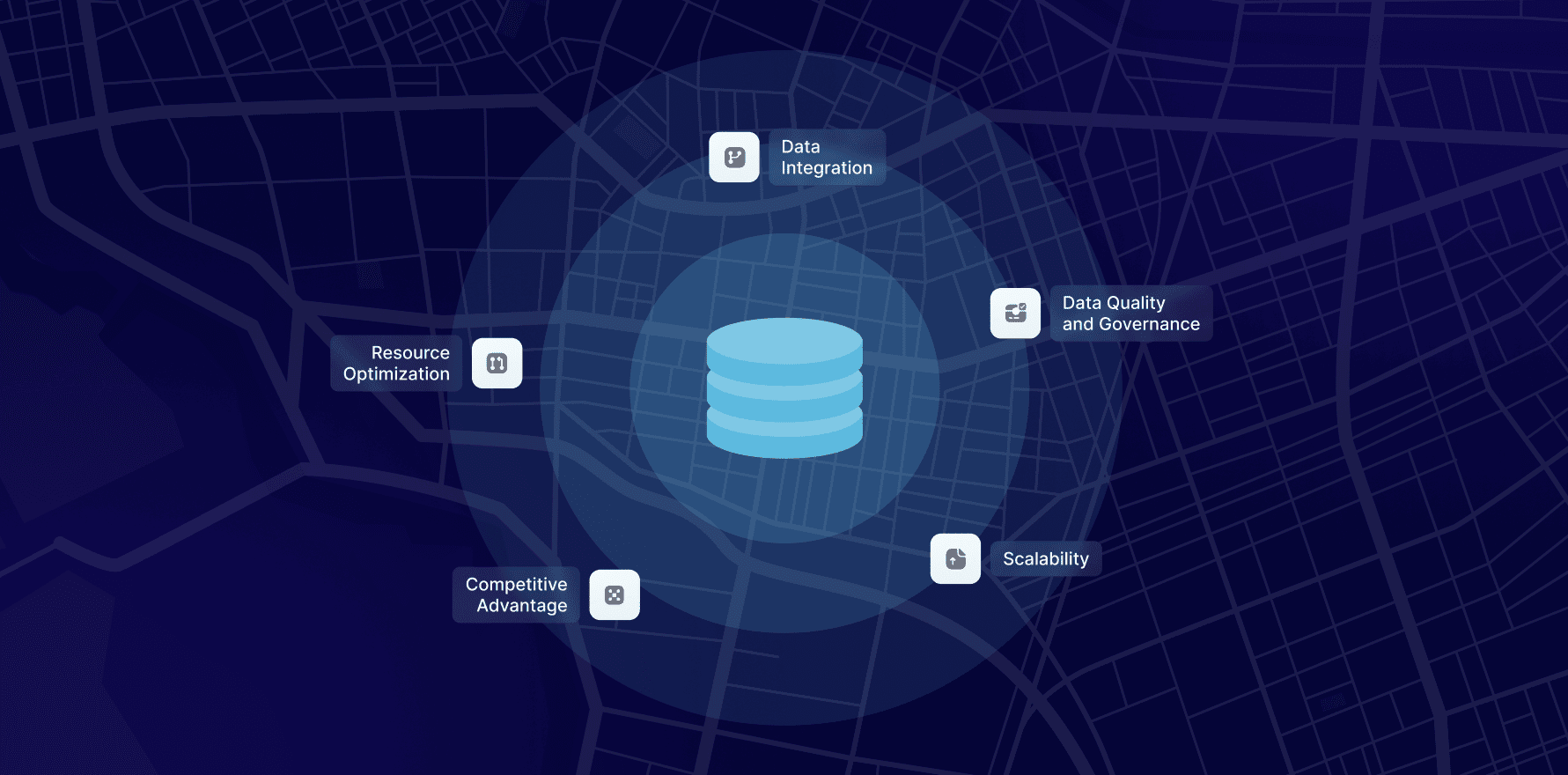
1. Data Integration
A data strategy ensures seamless integration of external and internal data sources. This creates a unified information view, enabling more comprehensive analysis and better decision-making.
2. Data Quality and Governance
A well-defined data strategy establishes data quality standards and governance frameworks. This ensures that external data is accurate, reliable, and used ethically, maintaining compliance with data protection regulations.
3. Scalability
As businesses grow, their data needs evolve. A scalable data strategy allows organizations to adapt to increasing data volumes and complexity, ensuring they can continue to leverage external data effectively.
4. Competitive Advantage
A strategic approach to data utilization positions businesses ahead of competitors. By leveraging external data insights, companies can anticipate market shifts, meet customer needs more effectively, and innovate continuously.
5. Resource Optimization
Implementing a data strategy helps allocate resources efficiently, ensuring that data collection, analysis, and application efforts are aligned with business goals. This maximizes the return on investment in data initiatives.
If you are looking to understand why your business need external data – Speak to our data expert
Implementing a Data Strategy
1. Define Objectives
Clearly outline what you aim to achieve with your data strategy. Objectives could include improving customer insights, enhancing product development, or optimizing operational efficiency.
2. Identify Data Sources
Determine which external data sources are most relevant to your objectives. This could include market research reports, social media data or, or reaching out to external data partners like Factori to source datasets like – POI data, Consumer data, Location data, Audience data, and Mobility data – check out all Factori data catalogs.
3. Data Integration Tools
Invest in tools and technologies that facilitate the integration of external and internal data. Data management platforms, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools, and APIs can help streamline this process.
4. Data Governance Framework
Establish policies and procedures for data quality, privacy, and security. Ensure that data usage complies with relevant regulations and industry standards.
5. Analytics Capabilities
Develop advanced analytics capabilities to extract actionable insights from data. Machine learning, AI, and predictive analytics can enhance your ability to leverage external data effectively.
6. Continuous Improvement
Review and refine your data strategy regularly. Stay updated with the latest data sources, tools, and best practices to ensure they remain effective and aligned with business goals.
Emerging Trends in External Data
Advancements in technology are reshaping how organizations leverage external data. Below are key trends driving adoption, along with examples of how leading companies are putting them into practice.
1. AI and Machine Learning–Driven Data Enrichment
AI and machine learning are increasingly used to transform raw external datasets into actionable insights, improving forecasting accuracy and decision-making at scale.
Example: Retail and e-commerce leaders use AI-enriched external signals—such as mobility and behavioral data—to personalize experiences, optimize pricing, and improve demand predictions.
2. Real-Time and High-Frequency External Data
Businesses are moving from static datasets to real-time or near–real-time external data to respond faster to changing conditions.
Example: On-demand and logistics platforms leverage live weather, traffic, and demand signals to dynamically adjust routing, pricing, and capacity planning.
3. Greater Focus on Data Privacy and Ethical Use
As external data usage grows, organizations are prioritizing privacy-safe data collection, governance, and compliance.
Example: Technology companies increasingly rely on aggregated and anonymized external data to enhance services while adhering to global data protection regulations.
4. External Data Embedded Directly into Forecasting Models
External data is no longer just contextual—it is now embedded directly into predictive and planning models.
Example: Businesses incorporate economic indicators, local events, and environmental data into forecasts to anticipate demand shifts and reduce uncertainty.
5. Seamless Integration with Modern Data Platforms
External data is increasingly delivered through APIs and cloud-native platforms, enabling faster integration into analytics and AI workflows.
Example: Enterprises integrate external datasets directly into their data lakes and BI tools to reduce time-to-insight and accelerate decision-making.
Built for Trust, Privacy, and Compliance
As external data becomes embedded in forecasting and decision systems, privacy and compliance are non-negotiable. Organizations must ensure that external data is sourced and processed responsibly, with safeguards that protect individual privacy while preserving analytical value.
At Factori, trust and governance are foundational to how external data is delivered and operationalized. Our data practices are designed to meet global regulatory and security standards, including:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
Ensuring lawful, transparent data collection and processing, with strong controls around consent, usage, and data minimization. - California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
Respecting consumer rights related to data access, deletion, and opt-out, while maintaining responsible data usage practices. - ISO 27001–Aligned Security Practices
Implementing rigorous information security controls to safeguard data across its lifecycle.
By prioritizing privacy-safe data sourcing, governance-by-design, and security best practices, Factori enables businesses to leverage external data confidently—without compromising compliance, ethics, or trust.
Conclusion
External data is a powerful asset that can drive business growth, innovation, and risk management. However, businesses need a robust data strategy to leverage its potential fully. By integrating external data with internal insights, maintaining data quality, and continuously refining their approach, organizations can gain a competitive edge and effectively navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape.
Want to learn more about how you can implement data strategy for your business? Schedule a free discovery call with our data experts and get personalized recommendations.
You may also like